As he languished in a Missouri prison for nearly three decades, Lamar Johnson never stopped fighting to prove his innocence, even when it meant doing much of the legal work himself.
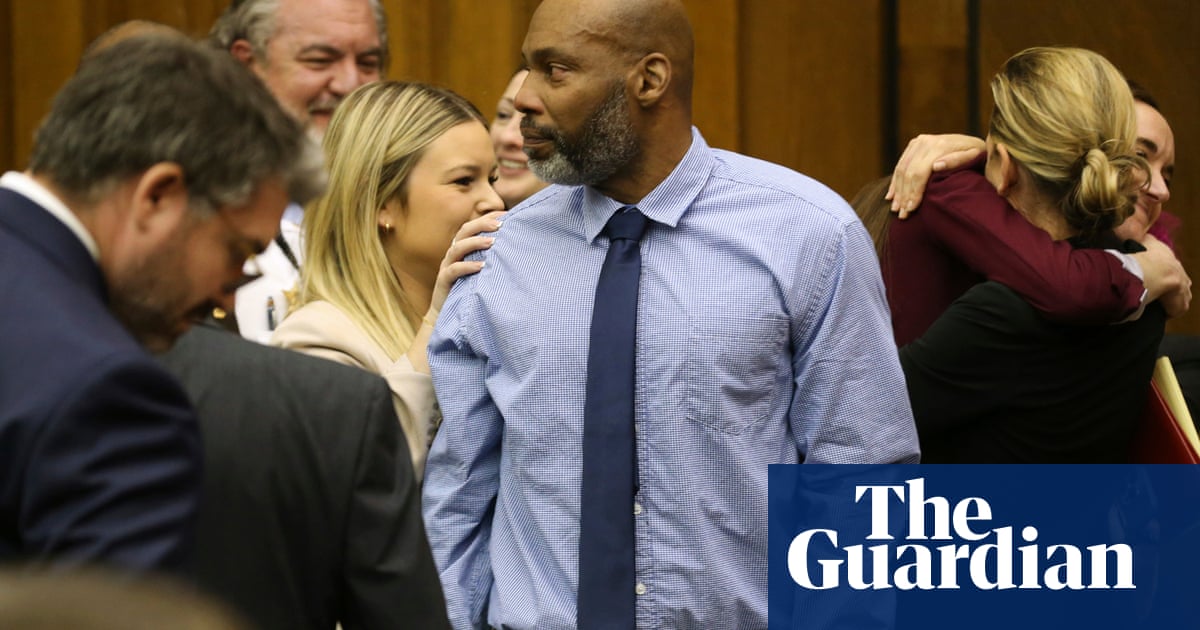
This week, a St Louis judge overturned Johnson’s murder conviction and ordered him freed. Johnson closed his eyes and shook his head, overcome with emotion. Shouts of joy rang out from the packed courtroom, and several people – relatives, civil rights activists and others – stood to cheer. Johnson’s lawyers hugged each other and him.
“I can’t say I knew it would happen, but I would never give up fighting for what I knew to be the right thing, that freedom was wrongfully taken from me,” Johnson said.
Thanks to a team of lawyers, a Missouri law that changed largely because of his case, and his own dogged determination, he can start to put his life back together. “It’s persistence,” the 49-year-old said Friday in an interview with the Associated Press.
“You have to distinguish yourself. I think the best way to get [the court’s] attention, or anyone’s attention, is to do much of the work yourself,” Johnson said. “That means making discovery requests from law enforcement agencies and the courts, and that’s what I did. I wrote everybody.”
He said he had been able to contact people “who were willing to come forward and tell the truth”.
Johnson was just 20 in 1994 when his friend Marcus Boyd was shot to death on Boyd’s front porch by two masked men. Police and prosecutors arrested Johnson days later, blaming the killing on a dispute over drug money.
From the outset, Johnson said he was innocent. His girlfriend backed his alibi that they were together when the killings occurred. The case against him was built largely on the account of an eyewitness who picked Johnson out of a police lineup and a jailhouse informant who told a police detective that he had overheard Johnson discussing the crime.
Decades of studies show that eyewitness testimony is right only about half the time – and since Johnson’s conviction, across the country there has been a re-examination of eyewitness identification procedures, which have been shown to often reproduce racial biases.
At a December hearing on Johnson’s innocence claim, the witness James Gregory Elking testified that the detective had “bullied” him into naming Johnson as a shooter, allegedly telling Elking, “I know you know who it is,” and urging him to “help get these guys off the street”.
The St Louis circuit judge David Mason also heard testimony calling into question the informant’s integrity. And James Howard, who is incarcerated at South Central correctional center in Licking, Missouri, came forward to tell the judge that he and another man had been the shooters – and that Johnson wasn’t involved. Howard is serving a life term for an unrelated murder.
After two months of review, Mason announced his ruling on Tuesday.
“It felt like a weight had been lifted off me,” Johnson said.
A connection to another wrongfully convicted man also led to Johnson’s freedom.
Ricky Kidd was convicted of killing two men in Kansas City in 1996. He was sent to the Potosi correctional center, where he and Johnson became friends. One day, in the prison yard, Johnson turned to Kidd.
“He said, ‘You might not believe me, but I’m innocent,’” Kidd recalled. “I said, ‘Oh yeah? You might not believe me but I’m innocent, too!’”
The two became cellmates. Eventually, the Midwest Innocence Project agreed to take on Kidd’s case. Meanwhile, Johnson’s effort was going nowhere. Kidd recalled a night when he was awakened by Johnson’s quiet sobs and the sound of his feet pacing the floor.
“He said, ‘Man, I don’t think I’m going to make it out. I keep getting these doors shut,’” Kidd said. “I said, ‘You got to hang in there’.”
Kidd talked to an Innocence Project investigator and made the case that since Johnson had already done so much background work himself, the process would have a head start. The organization took on his case.
The Kansas City attorney Lindsay Runnels, an Innocence Project partner, said Johnson’s work had been vital. For example, she said his Freedom of Information Act requests uncovered the extensive criminal background of the jailhouse informant, which called into question the man’s integrity.
“He just did all of that groundwork on his own from his jail cell, with nothing but paper and stamp,” Runnels said.
The St Louis prosecutor Kim Gardner believed Johnson was innocent. But her efforts to help him were blocked when the Missouri supreme court in March 2021 ruled that Gardner lacked the authority to seek a new trial so long – 28 years – after the conviction.
Missouri lawmakers, disturbed that an innocent person could remain in prison on that technicality, passed a law enacted in August 2021 that allows prosecutors to request a hearing before a judge in cases of potential wrongful conviction. That law freed another longtime inmate, Kevin Strickland, in 2021. He had served more than 40 years for a Kansas City triple-killing.
The Innocence Project’s website says that it has helped free or exonerate more than 240 people across the US, 58% of whom are Black.
DNA evidence exonerated most of them.
Kidd now is a public speaker who also works with prosecutors to help them avoid convicting innocent people. He hopes Johnson will join him in his effort, though it’s unclear what Johnson wants to do next.
“It’s exciting and a little intimidating,” he said. “I have to go out there and learn, and survive, and get my life back in order.”